Conquering Stent Restenosis
Advancing Solutions for Lasting Results
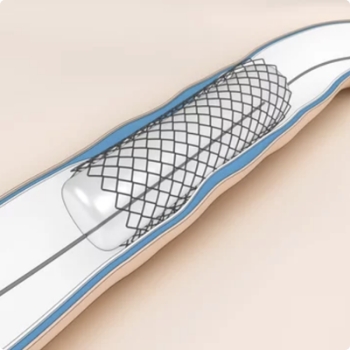
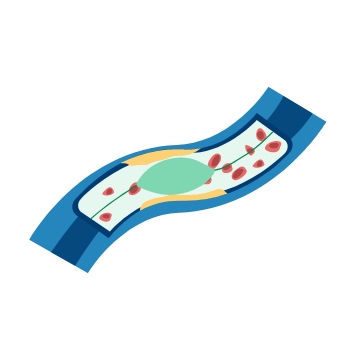
Stent Restenosis Mechanism and Its Symptoms
Treatment Options for Stent Restenosis
Repeat angioplasty can provide immediate relief by improving blood flow through the stent, alleviating symptoms. However, it may not address the underlying cause of restenosis – the accumulation of plaque or tissue. In cases where restenosis is due to excessive tissue growth, adjunctive treatments like drug-eluting balloons or cutting balloon angioplasty may be considered to enhance the long-term effectiveness of the procedure.
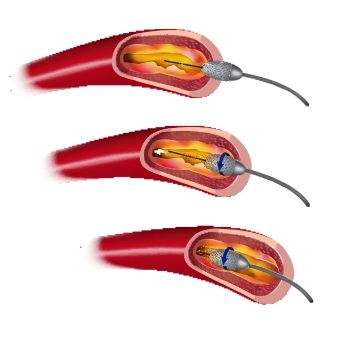
Cutting balloon angioplasty offers potential advantages over traditional angioplasty alone. By scoring the plaque or tissue, it aims to achieve better stent expansion and improve the long-term outcomes of the procedure. This technique is particularly useful when restenosis is caused by excessive tissue growth, as it can help prevent further narrowing.
Drug-eluting balloon angioplasty offers several potential benefits. The targeted delivery of medication can address the underlying cause of restenosis while still providing mechanical dilation of the stent. This approach aims to minimize tissue regrowth and improve the long-term effectiveness of the procedure. However, it’s important to note that drug-eluting balloon angioplasty is a relatively new technique, and further research is ongoing to fully understand its effectiveness and optimal use in treating stent restenosis.
These three treatment options – Repeat Angioplasty, Cutting Balloon Angioplasty, and Drug-Eluting Balloon Angioplasty – offer distinct approaches to managing stent restenosis. Repeat angioplasty provides immediate relief by mechanically opening the stent, while cutting balloon angioplasty scores the tissue to enhance stent expansion and prevent further narrowing. Drug-eluting balloon angioplasty delivers medication directly to the arterial walls, targeting tissue growth and promoting better long-term outcomes. The treatment depends on various factors, including the underlying cause of restenosis, the patient’s medical history, and the medical team’s expertise. Consulting with a healthcare provider is vital in determining each individual’s most suitable treatment approach.
How to Prevent Stent Restenosis after Angioplasty
Preventing stent restenosis is a crucial aspect of post-angioplasty care. While eliminating the risk may not be possible, certain measures help to reduce the likelihood of restenosis. Here are some tips to prevent stent restenosis:
Lifestyle Changes
Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle can significantly contribute to preventing restenosis. Quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight as well as engaging in physical activity, and following a balanced diet with less saturated fats and cholesterol are important steps to reduce the risk.
Manage Risk Factors
Control any underlying risk factors, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, or high cholesterol levels, through medication, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring. Managing these factors can help reduce the likelihood of restenosis.
Medication Adherence
Take all prescribed medications as your healthcare provider directs, especially antiplatelet drugs like aspirin or clopidogrel. These medications helps to prevent blood clots from forming within the stent.
Regular Follow-ups
Attend all follow-up appointments with your cardiologist as scheduled. These visits allow your doctor to monitor your progress, assess the stent’s condition, and make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
Remember, each case of stent restenosis is unique, and treatment decisions should be made in consultation with your healthcare provider. By understanding the mechanism of stent restenosis, being aware of the available treatment options, and taking preventive measures, you can optimize your chances of maintaining long-term stent patency and overall cardiovascular health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is stent restenosis?
Stent restenosis refers to the narrowing or blockage of a previously implanted stent in a blood vessel. It occurs when the inner lining of the blood vessel grows back over the stent, leading to reduced blood flow.
What are the symptoms of stent restenosis?
The symptoms of stent restenosis may include chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, reduced exercise tolerance, and a recurrence of symptoms similar to those experienced before the stent placement.
How common is stent restenosis?
Stent restenosis can vary depending on factors such as the type of stent used, patient characteristics, and the location of the stent. Advances in stent technology have significantly reduced the restenosis rate, but it can still occur in some cases.
What are the treatment options for stent restenosis?
The treatment options for stent restenosis include medication management, repeat angioplasty, the use of drug-eluting stents, and in severe cases, coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) surgery. Treatment choice depends on various factors and should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
Can medication prevent stent restenosis?
Medications, such as antiplatelet drugs, cholesterol-lowering agents, and blood pressure medications, can be prescribed to manage stent restenosis. These medications help prevent blood clots, reduce cholesterol levels, and control blood pressure, improving blood flow through the stent.
Subscribe to Platinum For Heart Newsletter
Sign up now and get free access to our monthly newsletter on Heart health & More
Sources:
1. www.medindia.net
2. www.apollohospitals.com
3. www.fortishealthcare.com
4. www.aiims.edu
5. www.maxhealthcare.in
Disclaimer: The information presented by Boston Scientific Corporation is for educational purposes only and does not recommend self-management of health issues. The information should not be treated as comprehensive and does not intend to provide diagnosis, treatment or any medical advice. Individual results may vary and hence, it is advisable to consult your doctor regarding any medical or health related diagnosis or treatment options.
IC-1659803AA-0823