Stent Procedure & Usage:
Understanding the Interventional Procedure in Heart for Coronary Artery Disease
Stent Procedure in Heart
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is an ailment affecting millions worldwide. It occurs when the blood vessels that supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked due to plaque buildup. It leads to chest pain, shortness of breath, and even heart attack. One of the treatments for CAD is the use of stents. Here, we will explore the use of stents in coronary artery disease, the stent procedure in the heart, and the interventional procedure involved.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a stent, and how is it used to treat coronary artery disease?
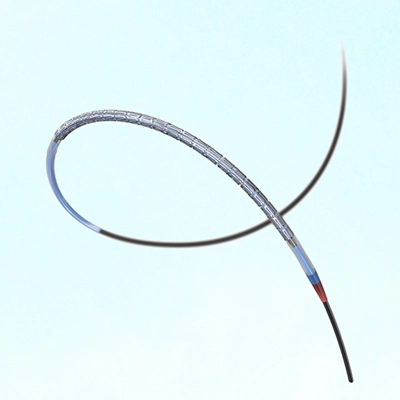
A stent is an expandable metal mesh tube to treat narrowed or blocked blood vessels, including coronary arteries. It is designed to hold open the artery walls and improve blood flow to the heart. The stent gets placed in the blocked artery during a stent procedure or coronary angioplasty, an interventional procedure used to treat coronary artery disease.
What is the stent procedure in heart, and how is it performed?
The stent procedure in the heart, known as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), is a minimally invasive procedure to treat narrowed or blocked coronary arteries effectively. During the procedure, a thin catheter gets inserted into an artery through the groin or wrist and guided to the blocked artery in the heart. A small balloon at the catheter’s tip gets inflated to help widen the artery and improve blood flow.
What are the risks and benefits of the stent procedure in heart?
Like any medical procedure, the stent procedure in heart comes with both risks and benefits. Some of the benefits of the stent procedure include improved blood flow to the heart, relief of chest pain, and reduced risk of heart attack. However, there are also risks associated with the procedure, such as bleeding, infection, and damage to the artery. In rare cases, stents can also become blocked or move out of place, requiring additional procedures or surgery.
Is the stent procedure in heart painful?
The stent procedure in the heart is usually performed under local anesthesia, meaning the patient is made awake during the procedure but does not feel pain. However, patients may experience some discomfort or pressure during the procedure. During this, the patients may experience soreness or discomfort at the site where the catheter was inserted.
Can the stent procedure in the heart be done on an outpatient basis?
Yes, the stent procedure in the heart is performed within a specified timeline, and the patient may make their way home the same day as the procedure. However, some patients may need to stay in the hospital overnight for observation.
Subscribe to Platinum For Heart Newsletter
Sign up now and get free access to our monthly newsletter on Heart health & More
Sources:
1. Max Healthcare: https://www.maxhealthcare.in/blogs/heart-health/stent-procedure-heart-disease
2. Apollo Hospitals: https://www.apollohospitals.com/lets-talk-health/heart-blocks-and-stenting
3. Fortis Healthcare: https://www.fortishealthcare.com/india/clinical-speciality/cardiac-sciences/stenting-52
4. Medanta: https://www.medanta.org/patient-education-blog/angioplasty-and-stent-placement
5. Narayana Health: https://www.narayanahealth.org/blog/coronary-stenting-angioplasty-a-brief-overview
Disclaimer: The information presented by Boston Scientific Corporation is for educational purposes only and does not recommend self-management of health issues. The information should not be treated as comprehensive and does not intend to provide diagnosis, treatment or any medical advice. Individual results may vary and hence, it is advisable to consult your doctor regarding any medical or health related diagnosis or treatment options.
IC-1626002AA-0623