Empowering Hearts with Biodegradable Solutions
Breakthroughs in stent technology with biodegradable polymers
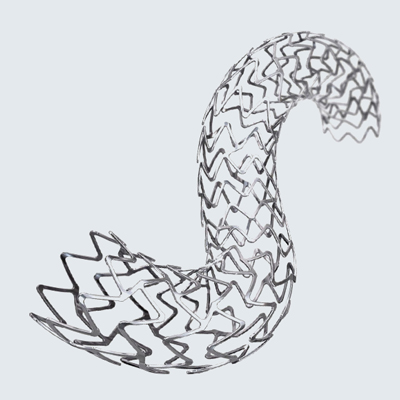
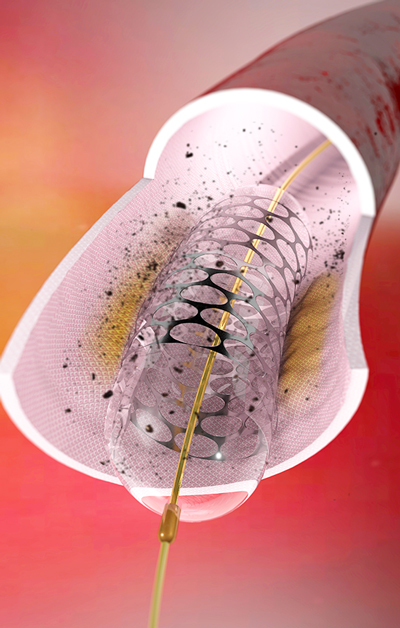
Biodegradable Polymer Drug-Eluting Stent
Benefits of Biodegradable Polymer Drug-Eluting Stents
Biodegradable polymer stents represent a significant breakthrough in the field of interventional cardiology. These innovative devices provide numerous advantages, including reduced long-term complications, minimized risk of restenosis, and simplified treatment procedures. The biodegradable polymer stent dissolves over time, promoting natural artery function and eliminating the need for additional invasive procedures.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a biodegradable polymer stent?
A biodegradable polymer stent is a medical device for treating coronary artery disease. It consists of a metallic scaffold for structural support and a biodegradable polymer coating that gradually releases medication into the arterial walls. Unlike permanent metal stents, biodegradable polymer stents are designed to dissolve over time, allowing the artery to regain its natural function.
How does a biodegradable polymer stent differ from a traditional stent?
The main difference between a biodegradable polymer stent and a traditional stent lies in its composition and behavior within the body. Biodegradable polymer stents are made with materials that gradually degrade over time, whereas traditional stents are typically made of permanent metals. Additionally, biodegradable polymer stents release medication to prevent restenosis, while traditional stents primarily act as a mechanical scaffold.
What are the advantages of Biodegradable Polymer Stent?
Biodegradable polymer stents offer several advantages over traditional stents. Firstly, they minimize the risk of long-term complications, such as late-stent thrombosis, as they dissolve over time, eliminating the need for stent removal procedures. Secondly, the controlled release of medication from the polymer coating reduces the occurrence of restenosis, improving long-term clinical outcomes. Additionally, the absence of a permanent metal implant simplifies imaging during follow-up evaluations.
How long does a biodegradable polymer stent take to dissolve?
The dissolution rate varies depending on the specific design and composition of the biodegradable polymer stent. Generally, the stent takes several months to a few years to fully dissolve. During this time, the artery gradually returns to its natural state, allowing for improved blood flow and reduced risk of complications.
Are biodegradable polymer stents as effective as traditional stents?
Biodegradable polymer stents have shown comparable effectiveness to traditional stents in clinical studies. They have demonstrated excellent short-term results regarding immediate vessel opening and reduced restenosis rates. Long-term studies are still ongoing to assess the durability and safety of biodegradable polymer stents over extended periods. However, early evidence suggests that these stents provide promising outcomes in improving patient care and reducing the need for additional interventions.
Subscribe to Platinum For Heart Newsletter
Sign up now and get free access to our monthly newsletter on Heart health & More
Sources:
1. www.indianheartassociation.org
2. www.aiims.edu
3. www.nicvd.org
Disclaimer: The information presented by Boston Scientific Corporation is for educational purposes only and does not recommend self-management of health issues. The information should not be treated as comprehensive and does not intend to provide diagnosis, treatment or any medical advice. Individual results may vary and hence, it is advisable to consult your doctor regarding any medical or health related diagnosis or treatment options.
IC-1659801AA-0823